Tubes and ferrule fittings are widely used in industries that require precise fluid and gas handling. Tubes typically have thinner walls and are more suitable for precise flow control and delicate systems, while ferrule fittings provide a secure, leak-proof connection in tubing systems.
Ferrule fittings (also known as compression fittings) are mechanical connectors used to join tubes and pipes without welding. They are especially valued for providing a secure, leak-proof seal in high-pressure applications.
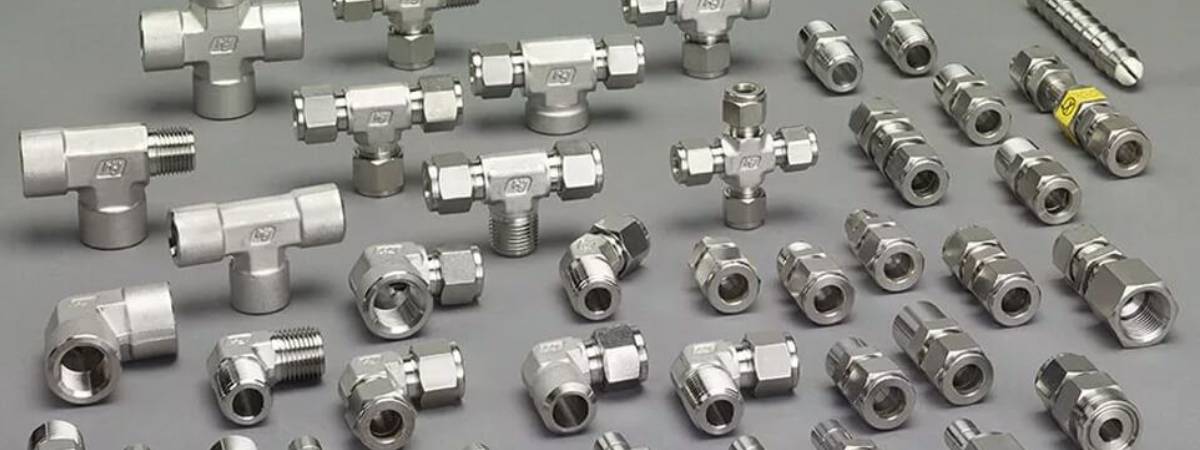

- Body: The main component of the fitting that houses the ferrules and tube.
- Nut: Screwed onto the body to compress the ferrules and create the seal.
- Ferrules: Rings (usually two, an inner and outer ferrule) that compress onto the tube when the nut is tightened, ensuring a leak-proof connection.
- Leak-Proof Sealing: Ferrule fittings provide a reliable, leak-proof seal for fluids and gases, even in high-pressure applications.
- Vibration Resistance: The double ferrule design, in particular, provides better resistance to vibration, ensuring the fitting remains securely connected under dynamic conditions.
- Reusability: Ferrule fittings can often be reused by replacing the ferrule, which helps in reducing overall system maintenance costs.
- Easy Installation: No welding, soldering, or brazing is needed. Ferrule fittings are typically installed using standard tools, making them a popular choice for quick and secure connections.
| Size: | Outside diameter (OD) and Wall thickness. |
| Material | Stainless Steel |
| Pressure Rating | Tubes have pressure ratings that indicate the maximum pressure they can safely withstand. The pressure rating depends on the material, wall thickness, and construction of the tube. |
| Temperature Rating | Tubes also have temperature ratings that indicate the maximum and minimum temperatures they can handle without compromising their structural integrity or performance. |