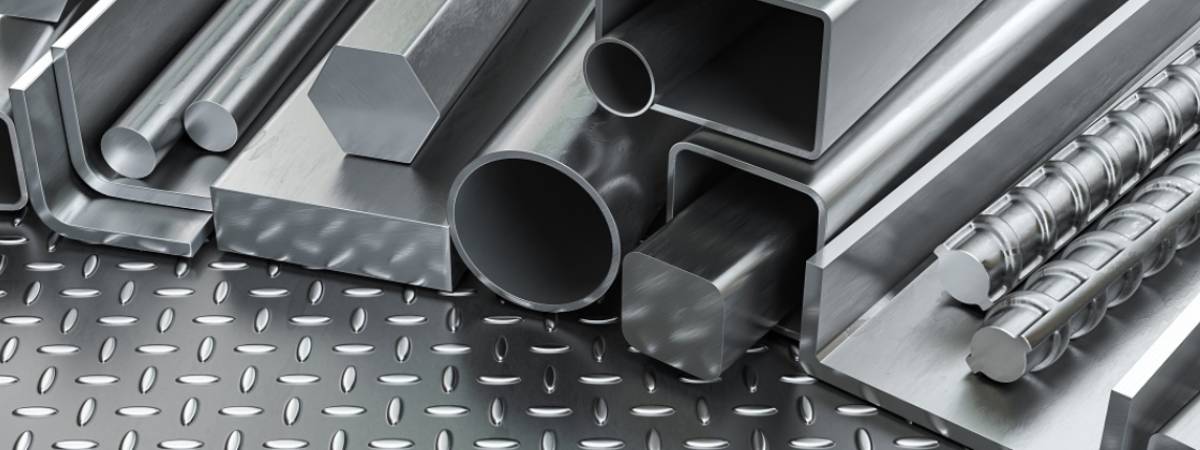
Structurals are steel products that are used in the construction of buildings, bridges, towers, and other load-bearing structures. These products are designed to bear heavy loads and provide strength and stability to various types of construction. Structural steel is valued for its strength, durability, and versatility, and it comes in various shapes and sizes to meet different engineering requirements.
Advantages of Structural Steel:
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio:Structural steel offers a higher strength-to-weight ratio compared to other construction materials like concrete or wood, making it ideal for large structures with minimal weight.
- Durability and Longevity: Steel is resistant to wear and tear, corrosion (when properly treated), and can last for decades, making it a cost-effective choice for long-term construction projects.
- Versatility: Structural steel comes in a variety of shapes and sizes, allowing engineers and architects to design and build complex structures with flexibility and creativity.
- Ease of Construction: Steel can be prefabricated off-site, reducing on-site construction time and labor costs. It also allows for quicker assembly, especially for large-scale projects.
- Recyclability: Steel is one of the most recycled materials globally, making structural steel an environmentally friendly option for sustainable construction.
- Fire and Weather Resistance: Structural steel can be treated to resist fire, and its inherent strength allows it to withstand extreme weather conditions like high winds and earthquakes.
Structural steel is an essential material in modern construction, offering unmatched strength, durability, and versatility. Whether it's high-rise buildings, bridges, industrial complexes, or large infrastructure projects, structural steel products like beams, channels, and tubes form the backbone of the world’s most ambitious and enduring structures. Selecting the right type of structural steel product depends on the specific engineering needs, such as load-bearing requirements, environmental conditions, and design specifications.
Specifications for Structural
| Structural Element |
Material |
Dimensions |
Design Criteria |
| Beams |
Steel |
I-beam, H-beam, T-beam |
Load-carrying capacity, allowable deflection, |
| Columns |
Concrete |
Rectangular, circular |
Load-carrying capacity, slenderness ratio |
| Slabs |
Reinforced |
Thickness, span |
Load-carrying capacity, deflection limits, crack |
| Walls |
CMU |
Thickness, height |
Load-carrying capacity, lateral stability, fire |
| Foundationss |
Concrete |
Depth, width, shape |
Load-carrying capacity, bearing capacity of soil |
Angles Weight Chart
| Size in mm |
Weight in Kg/m |
Size in mm |
Weight in Kg/m |
| 20 x 20 x 3 |
0.9 |
75 x 75 x 10 |
11.0 |
| 25 x 25 x 3 |
1.1 |
90 x 90 x 8 |
10.8 |
| 25 x 25 x 5 |
1.8 |
90 x 90 x 10 |
13.4 |
| Walls |
CMU |
Thickness, height |
Load-carrying capacity, lateral stability, fire |
| 30 x 30 x 3 |
1.4 |
100 x 100 x 6 |
9.2 |
| 35 x 35 x 5 |
2.6 |
100 x 100 x 8 |
12.1 |
| 40 x 40 x 3 |
1.8 |
100 x 100 x 10 |
14.9 |
| 40 x 40 x 5 |
3.0 |
100 x 100 x 12 |
17.7 |
| 40 x 40 x 6 |
3.5 |
110 x 110 x 8 |
13.4 |
| 50 x 50 x 5 |
3.8 |
110 x 110 x 10 |
16.5 |
| 50 x 50 x 6 |
4.5 |
130 x 130 x 10 |
19.7 |
| 65 x 65 x 6 |
5.8 |
130 x 130 x 12 |
23.4 |
| 65 x 65 x 8 |
7.7 |
150 x 150 x 10 |
22.8 |
| 65 x 65 x 10 |
9.4 |
150 x 150 x 12 |
27.2 |
| 75 x 75 x 6 |
6.8 |
200 x 200 x 12 |
36.6 |
| 75 x 75 x 8 |
8.9 |
- |
- |
Channel Weight Chart
| Designation |
Size mm x mm |
Weight Kg/m |
Weight Lb/ft |
| 75 |
75 x 40 |
6.8 |
4.57 |
| 100 |
100 x 50 |
9.2 |
6.18 |
| 125 |
125 x 65 |
12.8 |
8.60 |
| 150 |
150 x 75 |
16.4 |
11.02 |
| 175 |
175 x 75 |
19.2 |
12.90 |
| 200 |
200 x 75 |
22.2 |
14.92 |
| 225 |
225 x 80 |
26.0 |
17.4 |
| 250 |
250 x 80 |
30.4 |
20.42 |
| 300 |
300 x 90 |
35.9 |
24.13 |
| 350 |
350 x 100 |
42.2 |
28.36 |
| 400 |
400 x 100 |
49.5 |
33.26 |